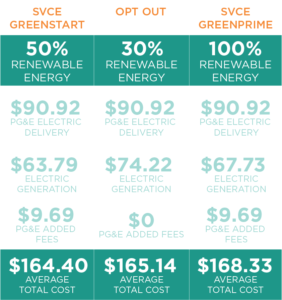
Multi-specialist models recreate the activity of an arrangement of heterogeneous specialists (creating units, organizations) connecting with one another, and building the cost cycle by matching the interest and supply on the lookout. This class incorporates cost-based models (or creation cost models, PCM), balance or game hypothetical methodologies (like the Nash-Cournot structure, supply capability harmony – SFE, key creation cost models – SPCM), and specialist-based models. Multi-specialist models by and large spotlight subjective issues instead of quantitative outcomes. They might give bits of knowledge with respect to whether costs will be above minor expenses, and how this could impact the players’ results. In any case, they present issues in the event that more quantitative ends must be drawn, especially in the event that cheap energy rates in Fort Worth costs must be anticipated with an elevated degree of accuracy.
Crucial models
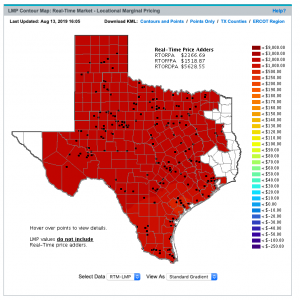
Crucial (primary) techniques attempt to catch the fundamental physical and financial connections which are available in the creation and exchange of power. The useful relationship between major drivers (loads, weather patterns, framework boundaries, and so on) is hypothesized, and the central information sources are displayed and anticipated freely, frequently by means of measurable, diminished structure, or computational insight procedures. As a general rule, two subclasses of major models can be recognized: boundary-rich models and closefisted underlying models of the organic market. Two significant difficulties emerge in the pragmatic execution of major models: information accessibility and consolidation of stochastic vacillations of the crucial drivers. In building the model, we make explicit suppositions about physical and financial connections in the commercial center, and thusly the cost projections created by the models are extremely delicate to infringement of these presumptions.
Decreased structure models
Scaled-down structure models portray the factual properties of power costs over the long haul, with a definitive target of subsidiaries’ valuation and hazard to the board. Their principal expectation isn’t to give precise hourly cost gauges, but instead to imitate the fundamental qualities of everyday power costs, such as peripheral dispersions at a future time focus, value elements, and connections between’s product costs. In the event that the cost cycle picked isn’t suitable for catching the principal properties of power costs, the outcomes from the model are probably going to be questionable. Nonetheless, assuming that the model is too complicated, the computational weight will forestall its utilization online in exchange offices. Contingent upon the sort of market viable decreased structure models can be named:
- Spot cost models give a tightfisted portrayal of the elements of spot costs. Their fundamental downside is the issue of evaluating subsidiaries, i.e., the distinguishing proof of the gamble premium connecting spot and forward costs. The two most well-known subclasses incorporate leap dispersion and Markov system exchanging models.
- Forward cost models consider the estimating of subordinates in a clear way (yet just of those composed on the forward cost of power). Nonetheless, they also have their restrictions; above all, the absence of information that can be utilized for alignment and the powerlessness to determine the properties of spot costs from the examination of forwarding bends.
Measurable models
Factual (econometric, specialized investigation) techniques gauge the ongoing cost by utilizing a numerical blend of the past costs or potentially past or current upsides of exogenous elements, regular utilization and creation figures, or climate factors. The two most significant classes are added substance and multiplicative models. They vary in whether the anticipated cost is the total (added substance) of various parts or the item (multiplicative) of various variables. The previous are undeniably more well known, however, the two are firmly related – a multiplicative model at costs can be changed into an added substance model at log costs. Measurable models are appealing in light of the fact that some actual translation might be connected to their parts, hence permitting designers and framework administrators to figure out their way of behaving.
Computational insight models
Computational knowledge (man-made brainpower based, AI, non-parametric, non-direct measurable) methods consolidate components of learning, development, and fluffiness to make moves that are equipped for adjusting to complex powerful frameworks, and might be viewed as “clever” in this sense. Counterfeit brain organizations, fluffy frameworks, and backing vector machines (SVM) are obviously the fundamental classes of computational knowledge strategies in EPF. Their significant strength is the capacity to deal with intricacy and non-linearity. By and large, computational knowledge strategies are better at demonstrating these highlights of power costs than measurable procedures.